What is CEFR and Where Did It Come From
The Council of Europe developed CEFR (Common European Framework of Reference for Languages) as an international system for standardized assessment of foreign language proficiency. This system is used worldwide to describe language knowledge levels.
CEFR is a scale that divides language level into six categories:
- A1 and A2 are beginner and elementary levels of language proficiency.
- B1 and B2 are intermediate and upper-intermediate levels.
- C1 and C2 are advanced and proficient levels of language proficiency.
This framework is used to describe what a person can do at each level: understand, read, speak, write, listen. However, CEFR does not provide a complete list of words distributed by levels, as the system evaluates broader aspects of language use, such as receptive and productive communication skills, not just vocabulary.
Interesting fact: CEFR was developed in 2001 and became a standard for assessing language skills in Europe and beyond. Today, 40 languages are standardized according to this system, and it is used in language schools, universities, and language certification worldwide.
Why There Is No Complete Word List for CEFR
CEFR focuses on competencies (for example, how a person uses language in real situations) and does not assign each word to a specific level. Ideally, for a real assessment of language knowledge level, it is important to consider context and functional skills.
At the same time, CEFR documents do not specify a single word list that would distribute all words of a language by levels. The system is not designed for this, as language vocabulary is dynamic, and word meanings depend on the context of their use.
Nevertheless, there are separate dictionaries in which words are assigned to CEFR levels. For example, the Oxford Dictionary presents a list of 5,000 words distributed across levels A1–C2. This dictionary is indicative and, despite its usefulness, is not comprehensive.
For comparison: an educated adult English speaker knows approximately 20,000 words actively, and passively (understands but doesn't use in speech) approximately 40,000 words.
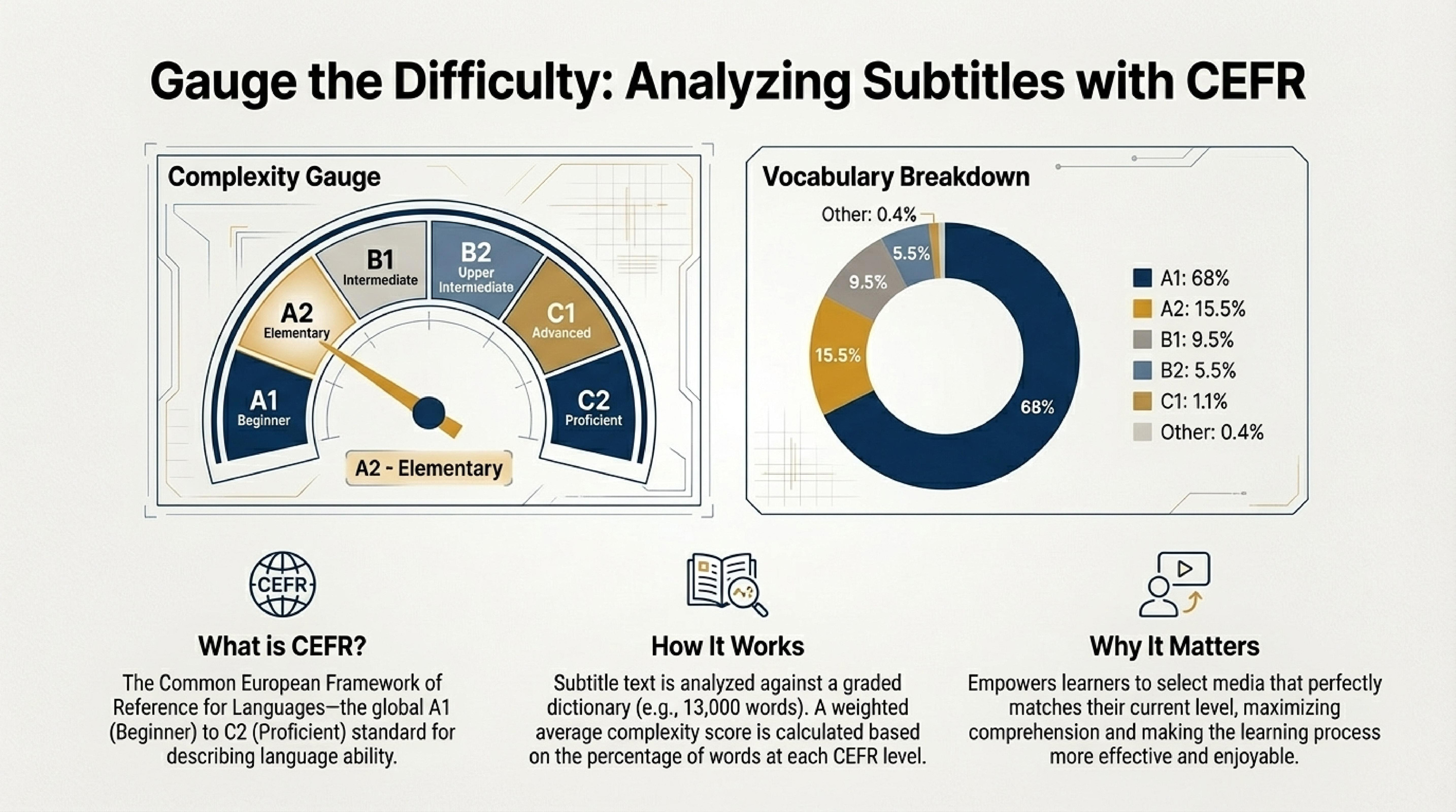
CEFR Level Calculation in This Service
This service analyzes subtitles (for example, from movies, TV series, educational videos) and assesses text complexity using a dictionary of 13,000 English words distributed by CEFR levels. The system is designed to assess lexical complexity of text based on its lexical composition.
How the service works:
- Analyzes subtitles — breaks them down into words.
- Each word is checked against the dictionary.
- Each word is assigned a CEFR level (A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2).
- Word distribution by levels is calculated, and based on this, the overall text complexity level is determined.
Approximate accuracy of the method:
With the current approach, the accuracy of lexical complexity assessment is approximately 80%. This indicator depends on the quality of the dictionary, as well as on the context features where words appear. This method allows for a quick approximate assessment of text complexity.
Formula for Calculating Weighted Average
To calculate the weighted average (averageWeight), which determines text complexity, the following formula is used:
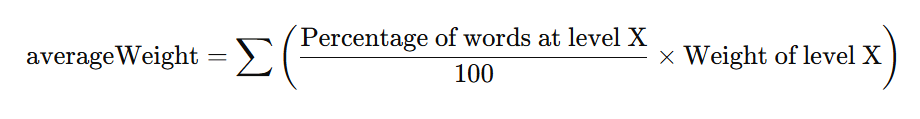
Where:
- Percentage of words at level X is the proportion of words in the text belonging to that level (for example, if 20% of words are A1, then the percentage of words at level A1 = 20).
- Weight of level X is a predetermined weight for that level (for example, for A1 weight = 1.5, for B2 weight = 6.5).
After calculating the weighted average, predetermined thresholds are used to determine the overall text complexity level. These thresholds allow assigning the obtained value to one of the CEFR levels (A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2). For example, if the weighted average is less than a certain threshold, the text belongs to level A1; if the value is between two thresholds, it belongs to the corresponding intermediate level, and so on.
Calculation example:
Suppose we have a text distributed as follows:
- A1: 68% → weight 1.5
- A2: 15.5% → weight 2.5
- B1: 9.5% → weight 4.5
- B2: 5.5% → weight 6.5
- C1: 1.1% → weight 8
- C2: 0.4% → weight 10
The sum of all percentages is 100%. Then the weighted average for this text is calculated as follows:
This value indicates level A2, as it falls within the range between thresholds for levels A2 and B1, but shows that vocabulary from levels A1 and A2 predominates.
How Accurate Is This Approach — Pros and Cons
✅ Advantages:
- Automation: Quick assessment of text complexity (subtitles or articles) based on vocabulary.
- Objectivity: Assessment based on predetermined weights and dictionary, results are always reproducible.
- Flexibility: Ability to configure dictionary and formulas for different text types (subtitles, scientific articles, technical documents).
- Practicality: Easy to determine how complex text is for language learners.
⚠️ Limitations:
- Vocabulary is not everything: Text complexity depends not only on vocabulary, but also on syntax, context, and style.
- Dictionary limitations: 13,000 words is a lot, but not complete language coverage. Especially lacking are rare and specialized terms.
- Context and polysemy: One word can be simple in one context and complex in another. For example, the word "bank" can be simple (financial institution) or complex (river or genetics).
- Genre features: Texts with colloquial language or terminology may give distorted results if genre is not taken into account.
Conclusion: Should You Trust This Assessment?
If you want to quickly and effectively assess text complexity (for example, subtitles or other vocabulary), then this service with a 13,000-word dictionary can provide a good approximate assessment. However, for a complete and accurate assessment of CEFR level, it is necessary to consider not only vocabulary, but also grammar, style, text structure, and the interaction of different language components.
Use this service as a tool for initial assessment, but for more accurate conclusions, it is always useful to combine it with other assessment methods.
Why Is CEFR Subtitle Complexity Analysis Needed on This Site?
Our subtitle merging service now includes a CEFR complexity analysis feature that helps:
- Choose appropriate content: Before merging subtitles, you can assess their complexity and understand if they suit your language knowledge level.
- Track progress: By analyzing the complexity of subtitles from different movies or TV series, you can see how your vocabulary grows and choose more complex content as you learn the language.
- Learn effectively: Knowing the complexity level of subtitles, you can choose materials that match your current level, making the learning process more effective and enjoyable.
- Plan learning: You can create a language learning plan, starting with subtitles at levels A1-A2 and gradually moving to more complex levels B1-B2 and C1-C2.
Tip: Combine CEFR complexity analysis with the subtitle merging feature to create the perfect language learning tool. Upload English and Russian subtitles, find out their complexity level, merge them into one file, and start learning the language with content that matches your level!